Vascular Complications of Diabetes
People living with diabetes have too much sugar in their blood and this changes the blood vessels to become narrow which give rise to various complication referred to as vascular complications of Diabetes.
In Ayurveda, this can be understood as when a person consumes too much sweet (Madhur such as excessive sugar), heavy (Guru such as Dairy, and Meat), channel blocking (Abhishyandi such as Curd and non-compatible meals), this results in excessive sugar accumulation in the body along with obstruction of free blood flow in the blood vessels.
All this results in high blood sugar levels and later on vascular complications of diabetes if the sugar levels stay high for a longer duration. This channel-blocking mechanism also leads to the formation of plaque that further gives rise to complications in the heart, brain, kidney, and almost every organ of the body.
As the old saying goes ‘The devil doesn’t come alone’, and the same can be said about Diabetes now also. This is precisely the reason that Diabetes has been called a group of chronic diseases and not just a single disease characterized as having only hyperglycemia or elevated sugar levels.
In Diabetes, the body has to multitask as in addition to ensuring the adequate delivery of glucose to the tissues of the body, the treatment focuses on lowering blood glucose levels. Hence, it becomes imperative to know what foods diabetics should eat to carry their days full of energy since excessive sugar or lack of sugar will impair their set of daily activities. The long-used diabetic diets suggested by the Western world have failed that ask you to reduce fat earlier and now making carbohydrates a monster. You just need to what kind of carbohydrates and fats you can consume.
If you are a patient of Diabetes or anyone around you is a diabetic, then you not only need to reverse/manage/control it soon, rather you need to be all wary of the complications it can bring in the future which is deadlier than Diabetes.
Types of Vascular Complications
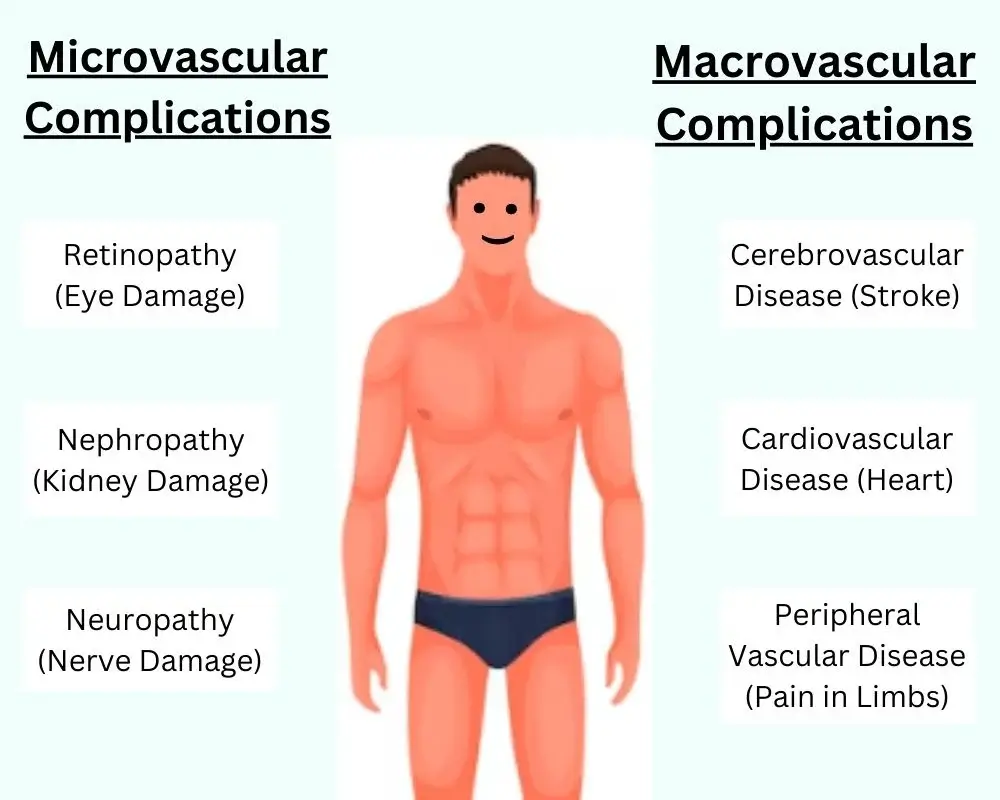
The two types of complications are defined as microvascular and macrovascular complications with further subtypes. While macrovascular disease affects large blood vessels, the microvascular disease affects smaller blood vessels, such as the capillaries.

Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
There are 3 major manifestations of microvascular disease, retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy:
- Diabetic Retinopathy-
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the most common microvascular complications of Diabetes. It is an eye condition that causes vision loss and blindness in people who have diabetes. It affects blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye).
The prolonged high blood sugar levels in the body lead to Diabetic retinopathy. The damage to the eyes happens when sugar blocks blood vessels leading to the retina, and to make up for these blocked vessels, eyes grow new blood vessels that don’t function well and leak or bleed easily.
It begins to develop as early as 7 years before the diagnosis of Diabetes in patients with type 2 diabetes. So, you must give a thought that even if your blood sugar reports are OK, you still need to be alert always and keep your artificial sugar intake in check.
Oxidative stress may also play an important role in cellular injury from hyperglycemia. High glucose levels can stimulate free radical production and reactive oxygen species formation. It is advisable to get dilated eye examination regularly (at least once a year). Patients with type-1, type-2, and even pregnant women (gestational diabetes) are at risk of Diabetic Retinopathy.
The other complications of Diabetic retinopathy are Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), Neovascular glaucoma, and retinal detachment.
- Diabetic Nephropathy-
Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of renal failure across the globe. In patients with diabetes, severe damage to the blood vessels carrying blood to the kidney can lead to diabetic nephropathy which impairs kidney functions. Our kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessels (glomeruli) that filter waste from our blood. Severe damage to these blood vessels can lead to diabetic nephropathy, decreased kidney function and kidney failure. The cost and trouble of diabetic patients needing dialysis are painful.
Diabetic nephropathy is defined by proteinuria > 500 mg in 24 hours in the setting of diabetes, but this is preceded by lower degrees of proteinuria, or “microalbuminuria. As many as 7% of patients with type 2 diabetes may already have microalbuminuria at the time they are diagnosed with diabetes but lack of awareness among patients on the complications of diabetes make them eat meals not good for their conditions and further deteriorate the vascular system of the body.
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. It’s also called diabetic kidney disease. In the United States, about 1 in 3 people living with diabetes have diabetic nephropathy and the trends are not encouraging in India as well which is not well equipped to deal with this gigantic economic burden of lifestyle disorders given an unequal, disparity of access to healthcare and with rising economic cost on seeking quality healthcare.
- Diabetic Neuropathy–
The damage to nerves resulting from hyperglycemia is referred to as diabetic neuropathy. The common symptoms of diabetic neuropathy include pain, burning, tingling, or numbness in the toes or feet and extreme sensitivity to light touch. In the Ayurveda text Charak Samhita, these are mentioned as Daah (burning), Paadsuptata (Numbness) and Vedna (Pain).
More than 80% of amputations occur after foot ulceration or injury, which can result from diabetic neuropathy.
Chronic sensorimotor distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most common form of neuropathy in diabetes. Typically, patients experience burning, tingling, and “electrical” pain, but sometimes they may experience simple numbness.
Macrovascular Complications
The macrovascular complications of diabetes happen as a buildup of fatty substances (plaque) that narrows the blood supply to the heart, brain and rest of the body. This narrowing process is called atherosclerosis and this is the central pathological mechanism in macrovascular disease.
Diabetes also increases the chances of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in an individual and CVD is the primary cause of death in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The condition also leads the big expenditures for diabetics. The other risk factors for CVD include are high blood pressure, high lipid levels, and belly fat.
Among other complications, diabetes has been named as a strong predictor of cerebrovascular disease and patients with diabetes type 2 have a higher risk for stroke. The stroke-related mortality is also higher in patients with diabetes. The goal of treatment should also focus on keeping a healthy heart and brain with blood pressure in check.
This blog is not to frighten you but to firm your resolve and fight out any complicated condition that you are facing right now. All this significantly concludes that diabetes doesn’t come alone, so it doesn’t go with medicines alone, you need to adopt a comprehensive, wholesome, holistic Ayurvedic Treatment for Diabetes to counter its complications.
Remember, medicine is just one pillar of the treatment, the other two are Regimen and Lifestyle which sadly most of us leave for tomorrow and that tomorrow never comes.
START NOW!