Do You Know Everything About Diabetes?

‘Diabetes cannot be cured but managed!’
This phrase defines the most conveniently served lies of the past decades, which we have learned while growing up. Constant reiterations from the medical doctors, researchers, pharmaceutical companies have only fueled the acceptance of this fib by the gullible people worldwide, resulting in a pill-popping culture. The panic roused with this disease called Diabetes further thwarted any insights towards its reversal by metabolic correction measures described in the natural system of medicine like Ayurveda.
What if you have been told that living without consuming these sugar-controlling popping pills is very much possible.
No, it is not some futuristic statement loaded with just overpromised tone; this is a fact that has been endorsed by researchers and even the doctors of western and modern medical science. Some groundbreaking research as published by Dr. Neal D Barnard, MD; Dr. Alexa Fleckenstein, MD; Gabriel Cousens, MD; and others on reversing Diabetes is a straw in the wind!
Before we go into the cure, let us first understand what Diabetes is as a disease.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus or DM, if we define it, is a group of metabolic disorders affecting the body’s carbohydrate metabolism characterized by Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar), which usually results from defective insulin secretion, insulin resistance, or both.
Insulin, a key player in carbohydrate metabolism, is a hormone produced by the Beta-cells situated in the Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. Akin to these Beta Cells are the Alpha Cells which are responsible for the secretion of Glucagon. These glucosensitive Alpha and Beta-cells are the smart cells that produce automated responses according to blood-glucose concentration by releasing or suppressing the production of Glucagon and Insulin, respectively. Insulin helps reduce blood glucose levels by increasing glucose utilization by the body’s cells to produce energy. In contrast, Glucagon helps increase blood glucose levels by stimulating the liver to break down glucose (glycogenolysis) and glucose (gluconeogenesis).
Destruction of these Beta Cells due to autoimmune reactions or any injury leads to disruptions in insulin activity, leading to hyperglycemia. Other than that, condition like insulin resistance, when the body’s cells fail to respond to Insulin, is a contributing metabolic factor of Diabetes resulting from a sedentary lifestyle.
Both mechanisms either independently or cohesively result in different forms of Diabetes Mellitus!
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes (Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus or IDDM)
- Previously known as juvenile-onset Diabetes as it commonly affects children, but it can also occur in adults.
- An autoimmune disease characterized by faulty insulin production due to the destruction of Beta cells of the pancreas.
- Chronic multisystem disease affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins due to Insulin deficiency.
2. Type 2 Diabetes (Non- Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus or NIDDM)
- The most typical form of Diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia.
- Metabolic and lifestyle disorder arising due to a combination of insulin deficiency, resistance, and impaired glucagon production.
- It is usually a non-insulin-dependent form of Diabetes, but complications may lead to dependence on Insulin.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes is characterized by glucose intolerance during pregnancy.
- Underlying insulin resistance coupled with impaired insulin production is the causative factors leading to Gestational Diabetes.
- It commonly occurs in late pregnancy due to physiological changes such as reduced glucose uptake by skeletal muscle tissues.
General Symptoms
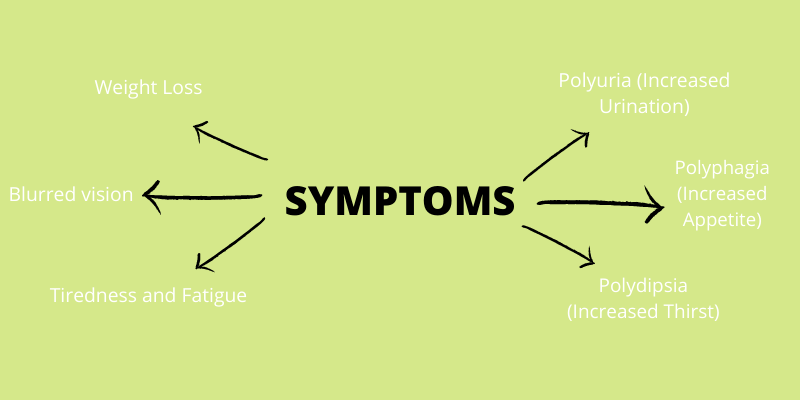
The common symptoms of Diabetes are –
- Polyuria (Increased Urination)
- Polydipsia (Increased Thirst)
- Polyphagia (Increased Appetite)
- Weight Loss
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Numbness in legs and feet
- Blurred vision
- Delayed wound healing.
Notably, the development of the symptoms in Type 1 DM is relatively rapid as compared to Type 2 DM.
Symptoms in Men vs Symptoms in Women
Symptoms of Diabetes are usually standard irrespective of gender. However, sure gender-specific signs require attention when we talk of Diabetes.
Symptoms in Men
- Low testosterone levels
- Erectile dysfunction
- Impotence
- Increased deposition of visceral fat
- Loss of muscle mass
Symptoms in Women
- High testosterone levels
- PCOS
- Early menopause
- Genital infections
- Increased risk of UTI
Diabetes in Children vs Diabetes in Adults
Diabetes is one such disease with occurrence in both children and adults. Even though all types of Diabetes Mellitus are similar, the effects and symptoms manifested in different age groups vary.
Symptoms in Children
- Usually at risk of developing Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus but can also suffer from Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Increased incidence of dehydration due to frequent urination
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Episodes of abdominal pain
- Mood swings
- Tiredness & rapid breathing
- Blurred vision
Symptoms in Adults
- Usually at risk of developing Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus but can also suffer from Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Dryness in mouth
- Unexplained weight loss despite good appetite
- Visual changes
- Pain and numbness in hand and feet
- Delayed wound healing
Causes of Diabetes
Causes of Diabetes varies according to ethnicity, genetic and family history, Health, and environmental factors. Type 1 Diabetes usually results from Insulin deficiency, whereas Insulin resistance is to be blamed for Type 2 Diabetes. However, there could be various factors specific to the individual, resulting in the causation of Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Causes
Insulin Deficiency can occur due to the destruction of Insulin forming Beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. The causes responsible for this could be –
- Autoimmune reaction
- Viral or bacterial infection
- Toxicity due to certain chemicals or food
- Injury or trauma to the pancreas
- Tumour or Carcinoma of the pancreas
Type 2 Diabetes Causes
Type 2 or Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus is a multifactorial pathology arising due to a combination of Insulin deficiency and resistance, which can be stimulated due to these factors –
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history
- An improper and inadequate diet consisting of junk and processed food
- Hypertension
- High Cholesterol
Gestational Diabetes Causes
Gestational Diabetes usually occurs due to insulin deficiency during the latter half of the pregnancy. Some of its probable causes are –
- Obesity
- Underlying insulin resistance
- PCOS
- Family history
- Large baby weighing 4.5 kg or more.
Diabetes Risk Factors
- Family history of Diabetes
- Obesity
- Ageing
- Hypertension
- Poor control on glucose intake
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
- Bad liver function
- Disrupted sleep pattern
- Stress
- Dependence on junk and processed food
- Intake of a diet devoid of fibre
Diabetes complications
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that is not confined to a system-specific. Its effects and even complications can be seen in all parts and systems of the body. These complications of Diabetes may be rapid or acute.
Acute Complications of Diabetes
- Hypoglycemia –
Hypoglycemia or low blood glucose is an acute complication in diabetics arising from factors resulting in too much glucose-lowering in the blood. It is characterized by agitation, sweating, cold and clammy limbs and cause loss of consciousness and even death!
- Diabetic ketoacidosis –
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a severe complication in which the liver starts breaking fats into the ketone bodies to compensate for low energy levels due to insulin deficiency. It is a medical emergency that leads to hypotension and shock followed by death!
- Nonketotic hyperosmolar coma –
This condition usually arises due to high blood glucose levels of 300mg/dl or more. The body compensates by drawing out all the water from the cells into the blood resulting in severe dehydration.
Chronic Complications of Diabetes
- Diabetic Nephropathy – Diabetes mellitus resulting in damage to the kidneys is termed Diabetic Nephropathy.
- Diabetic Neuropathy – Loss of sensation in extremities due to inherent nerve damage caused by Diabetes is termed Diabetic Neuropathy. It is a rather serious condition that can result in complications like Diabetic foot leading to amputation of the limb.
- Diabetic Amyotrophy – Weakness of muscles caused by diabetic neuropathy is termed Diabetic Amyotrophy.
- Diabetic Retinopathy – Diabetic Retinopathy is characterized by developing weak and friable blood vessels in the retina, prone to breakage and ultimately causes blindness.
- Diabetic Encephalopathy – Diabetic encephalopathy occurs due to altered vascular supply of the brain in diabetics.
- Diabetic Cardiomyopathy – Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart muscles undergo damage due to impaired relaxation and diastolic dysfunction, further leading to cardiac failure.
- Infertility – Infertility in both males and females is one of the most common chronic complications of Diabetes.
- Immunodeficiency – Diabetes due to impaired metabolism put the sufferers at an increased risk of respiratory infections and lung diseases.
Diabetes Tests & Diagnosis
Both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes can be diagnosed by some simple tests such as –
1. Random Blood Sugar –
- A random blood sugar reading of 200 mg/dL or higher in two consecutive tests indicates Diabetes.
2. Fasting Blood Sugar –
- Regular fasting blood sugar readings are less than 100 mg/ dL.
- Fasting blood sugar readings from 100 to 125 mg/dL are considered Prediabetic.
- Diabetes is confirmed if two consecutive tests readings are higher than 126 mg/dL.
3. Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) –
- HbA1c below 5.7 is considered normal.
- HbA1c values between 5.7 to 6.4 are indicative of Pre-Diabetes.
- HbA1c levels of 6.5 in two consecutive tests suggest that the individual is Diabetic.
4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test –
- Normal OGGT readings are 140 mg/dL or less.
- Prediabetes is confirmed if the readings are between 140 mg/dL to 200 mg/dL.
- A reading of 200 mg/dL after two hours of OGGT indicates Diabetes.
Who should get tested –
Those who are at risk of developing Diabetes should get themselves tested periodically.
- Obese and those with BMI higher than 25 should get their checkups done periodically.
- Those who have stepped in their 40s are recommended to undergo testing every year.
- Prediabetics are at risk of developing Diabetes and hence suggested to undergo testing every six months.
- Women with a history of gestational Diabetes are recommended to keep track of their blood sugar levels.
- Those suffering from Hypertension or Dyslipidemia are the risk factors for Diabetes. Such individuals should keep a tab on their blood sugar levels.
Limitations of Allopathic Treatment for Diabetes
The most significant limitation of the conventional pharmacotherapeutic practices for Diabetes is that they are focused on managing the blood sugar levels instead of hitting on the cause. This fact cannot be neglected that the side effects produced by these hypoglycemic drugs further deteriorate the quality of life of a diabetic individual. The primary cons of the allopathic treatment for Diabetes are enlisted below –
1. Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, as stated earlier, is the most dangerous complication of Diabetes arising due to decreased blood sugar levels. It is a fatal condition that affects both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetics equally. Aggressive insulin therapy coupled and unmanaged doses of antidiabetic drugs result in lowered blood sugar levels. It is not difficult to ascertain that every 1 in 10 Diabetic dies due to Hypoglycemia.
2. Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious Anemia is a condition that arises from vitamin B12 deficiency leading to decreased production of red blood cells. Metformin, the most prescribed oral hypoglycemic drug for the management of Diabetes, is responsible for irreversible nerve damage and memory impairment. It inhibits the absorption of Vit B12 from the gut by stimulating the growth of bacteria, reducing the motility of the small intestine.
3. Increased Risk of Malignancy
Hypoglycemic drugs like Metformin, Sulphonylureas, Glitazones, Insulin and its analogues, as per various research, have been linked with increased cancer growth. The increased detection of cancer in the population suffering from Diabetes is alarming. These allopathic drugs with mitogenic properties promote the growth of tumour cells. Diabetes is the 12th leading cause of death if we talk of global numbers, whereas cancer stands on number 2. The mortality rate in people with Diabetes suffering from cancer can be easily judged as tremendous.
4. Gradual deterioration of Health
Hypoglycemic drugs used for lowering down the blood sugar levels are filled with arrays of knock-on effects enough to make a sick person sicker! Constant stomach upsets, rashes, dizziness, metallic taste in the mouth, weight gain, puffy face, swelling in arms and legs are the common symptoms enough to deteriorate the quality of life in an otherwise happy individual!
Diabetes and Diet
Why Should Diabetics Have a Daily Diet Menu? Diet plays a significant role in managing disease, and food, if eaten right, can yield astounding health benefits. In disorders like Diabetes which affects carbohydrate metabolism, food plays a vital role in its effective management.
Do’s –
- Intake of complex carbs like whole wheat, quinoa, brown rice, oats.
- Plant-based proteins in the form of beans and lentils
- Seasonal fruits and leafy green vegetables
- Nuts including flaxseed and fibre-rich chia seeds
- Low-fat dairy products
- Vegetable oils like mustard, sunflower, sesame, olive
Don’ts –
- Foods with a high glycemic index like sugar, refined flour, corn.
- Canned, processed and junk food
- Vegetables with an excessive amount of starch in them.
- Fruits form mucus in the body.
- Fried meat, pork, bacon.
- Full fat dairy
- Trans and saturated fats
Diabetes Prevention
The prevention of Diabetes should begin as early as possible because the disease is progressive. Once a person gets diagnosed with Diabetes, and he/she does not opt to reverse the condition early. It will lead to ‘Type-1’ diabetes eventually, where insulin administration becomes a necessity. The simple ways to prevent Diabetes are as follows-
1. Maintain a healthy weight as per the body’s frame: Losing weight gradually in the healthiest way is what it requires to prevent Diabetes. The risk of developing diabetes in overweight people is five times higher in the obese than the people who are not obese.
So, suppose you are overweight and reading this article. In that case, the first thing you should do is to start putting off in a process and phase-wise manner and make sure the weight loss happens most healthily, not like the way it is being advocated by the big multi-level market brands available in the market who advocate drinking some protein shakes while snatching healthy fat from your body and putting you on the more significant risk of developing more harmful medical ailments/conditions.
2. Regular Personalized Workout: Follow the principle of ‘Earn but Burn’ that helps you burn the calories in the day. There are specified yoga asanas that have helped patients across the globe reverse the condition of Diabetes as they help the pancreas secrete more insulin in the body and also help in increasing body sensitivity.
3. Cutting on sugar: Unfortunately, we are eating 30 times more sugar today than we were eating 30 years back. All thanks to the global, unseasonal platters from every continent available around us. The processed and easy meals available in the form of bread, bakery edibles have made it impossible to reverse the condition of Diabetes.
Types of Diabetes According to Ayurveda
Diabetes, as per Ayurveda is classified under the Prameha group of disorders that primarily affect Basti, one of the three vital organs. This Prameha is a Kapha Dosha predominant disorder occurring due to varied etiologies, mostly sedentary lifestyle. These twenty types of Prameha Roga are divided into three groups as per their ‘Dosha‘ dominance which is as follows.
Kapha Prameha:
There are ten types of ‘Kaphaj Prameha’ as follows-
- Udakmeha – Diabetes Insipidus – Characterized by the discharge of relaxed, white, odourless, and transparent urine.
- Ikshumeha – Alimentary Glycosuria – Urine discharge with characteristic like sugarcane juice is observed.
- Sandrameha – Phosphaturia – Urine becomes viscous when left overnight.
- Sandraprasadmeha – Urine appears to be partly cloudy and partly clear when left overnight.
- Shuklameha – Chyluria – Opaque urine is passed out in this condition.
- Shukrameha – Spermaturia – Urine mixed with seminal discharge is observed.
- Sheetameha – Renal Glycosuria – There is the complaint of frequent bouts of cold urine.
- Shanaihmeha – The presence of concretions is seen along with urine.
- Salameh – Urine is passed out in smaller batches that too with incredible difficulty.
- Siktameha – Albuminuria – Slimy phlegm like urine is passed out.
Pitta Prameha-
There are six types of ‘Kaphaj Prameha’ as following-
- Ksharameha – Putrid smelling with alkaline nature is passed out.
- Kalameha – Urine with black discolouration is observed.
- Neelameha – Indicanuria – Blue urine is seen in such a condition.
- Haridrameha – Bilirubinuria – Yellow colour urine is passed out.
- Manjishthameha – Hemoglobinuria – The discharge of red colour urine characterizes it.
- Raktameha – Hematuria – The presence of red blood cells is observed in such a condition.
Vataj Prameha:
There are four types of ‘Kaphaj Prameha’ as follows-
- Majjameha – Urine mixed with Majja is seen.
- Vasantha – There is a presence of Vasa in urine.
- Madhumeha – Characterized by the discharge of sweet and astringent urine.
- Hastimeha – Urine is passed in large amount in such condition.
How Ayurveda Treats Diabetes?
While millions of people worldwide are getting affected by this disease, some thousands who research and search for its treatment have been successfully found a cure and able to reverse their condition of ‘Diabetes Mellitus’. The Ayurvedic treatment of Diabetes should follow the three pillars approach or principle of Ayurveda, namely-
1. Correction of Diet (Aahar)
While one goes for the ayurvedic treatment of Diabetes, it becomes imperative to choose the diet as per the aggravated ‘Dosha’ in the body. It is easy to choose the complex carbohydrates from the variety of carbohydrates available, but your gut needs to process them, which happens only when your digestive fire(Agni) burns simple and complex carbohydrates. It will be a surprise to know that even minute changes as removing dairy products from the regimen of people with Diabetes help control their Diabetes in a much faster way.
There are many more principles of Ayurveda dietetics involved in reversing the condition of Diabetes, which seldom appear in the list of even highly skilled modern nutritionists and dietitians, simply because they do not assess your Ayurveda Prakriti and body type before drafting your dietary regimen.
2. Correction of Lifestyle (Vihar)
One of the biggest contributors to this metabolic disorder is today’s sedentary lifestyle, including working on a computer, mobiles, and irregular sleeping patterns for long hours. The reversal of Diabetes requires a personalized workout plan that helps increase insulin sensitivity of the body. It stimulates the functioning of the pancreas in a better way, making your body process and burns sugar better, which helps you cut off your diabetic medications.
3. Administration of Ausdha (Medicines)
Unlike modern medicines, which either work on inhibiting sugar production or increasing more Insulin in the body. However, both Insulin or diabetic medicines as Glucophage help control the increased sugar levels in the body, but they bring other complications if continued for a more extended period. The Ayurvedic medicines, on the contrary, have a more significant and more profound role in reversing Diabetes, not merely controlling it with the best part that it helps a patient to completely stop the diabetic medicines once he or she fully gets recovered.
Personalized Diabetes Reversal Program
Every individual looks differently, and his/her gut behaves differently, and the reason precisely lies in their Prakriti/constitution. A skilled Ayurveda physician takes the help of this Ayurveda Prakriti to plan your diabetic dietary regimen that suits your daily schedule, eating habits and most importantly, your gut. Striving on the pillars of patient education, patient engagement, and patient empathy, the regimen from Aas Ayurveda has been helping people in reversing their Diabetes and living medicines-free life.






Thanks for your blog, nice to read. Do not stop.