Hair Loss

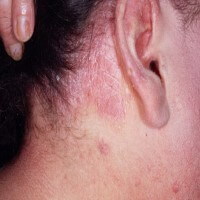
Psoriasis is a chronic recurring disease of the skin. It is characterized by the appearance of plaques, patches, or papules on the surface of the skin. The lesions are usually slightly elevated above the normal skin surface, sharply distinguishable from normal skin, and red to reddish-brown in color. They are usually covered with small whitish-silver scales…

Bronchitis is a common respiratory disorder in which the mucous lining of the respiratory passage and bronchioles gets inflamed. Bronchitis is of two types- Acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis or chest cold is the short-term inflammation of the bronchioles of the lungs; mostly the cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection. It lasts for…